The main aim of all laboratories is to produce reliable, reproducible, and timely results – particularly relevant within clinical and diagnostic laboratories 1. In order to achieve this, an efficient and coordinated workflow must be maintained, both within the lab internally, and with other labs and services externally 1. Inefficient laboratory workflows can be costly in terms of time and resources, but can also have a substantial negative impact on patients and diagnostic services.
Fortunately, strategies are available to improve laboratory workflows using automation. This article will explore what is meant by laboratory workflow, why workflow management is important, and how laboratory workflows can be improved through automation.
What is a laboratory workflow?
A laboratory workflow is a set of rules and systems designed to optimise efficiency and maximise laboratory output. An example of laboratory workflow management is LIMS (Lab Information Management System), a software and hardware solution designed to manage large numbers of samples and the data that is associated with it, leading to a more streamlined, efficient workflow. In clinical labs, efficient workflow strategies allow fast, reliable, and reproducible results to be generated, benefitting both the lab and the patient.
Why is laboratory workflow management important?
To keep up with clinical demand, laboratories must establish and maintain a high level of quality control in all laboratory processes, whilst also focusing on reducing costs wherever possible. This puts a significant amount of pressure on clinical labs; they are expected to handle increasing workloads and more varied assays, with the same amount (or less) staff 2.
Clinical laboratories only receive a small percentage of healthcare funding but influence up to 70% of medical decisions 2. It is therefore essential for clinical labs to provide quality results, whilst adhering to short turnaround times and also aiming to reduce costs wherever possible 3.
Improving laboratory workflow has emerged as an effective method of managing increased clinical demand. Key to laboratory workflow management is simplifying entire lab processes, eliminating wasteful steps while focusing on value and improving performance 2.
How can lab workflows be improved?
Several key areas have been identified that can help to improve laboratory workflows:
Identifying bottlenecks
Identifying bottlenecks within a lab, or obstacles that decrease lab efficiency, is often the first step to improving lab workflows. This can be done using bottleneck analysis, a step-wise approach that identifies the obstacles that stop a health system from achieving its desired impact 4. Bottleneck analysis examines all process steps from start to finish, determines a target value for each process (throughput, turnaround time), and identifies workflow constraints and the underlying causes 4.
Standardising workflows
An effective method of improving laboratory workflows is to standardise all of the experimental procedures performed in the lab. Standardisation is commonly implemented through standard operating procedures (SOPs), written step-by-step instructions for every experiment and analytical procedure carried out within a lab 5. By harmonising laboratory processes and reducing user errors, SOPs ensure consistency, accuracy, and quality of results produced 5. SOPs also help labs to adhere to standards and international regulations, such as ISO certification 5.
Laboratory workflow automation
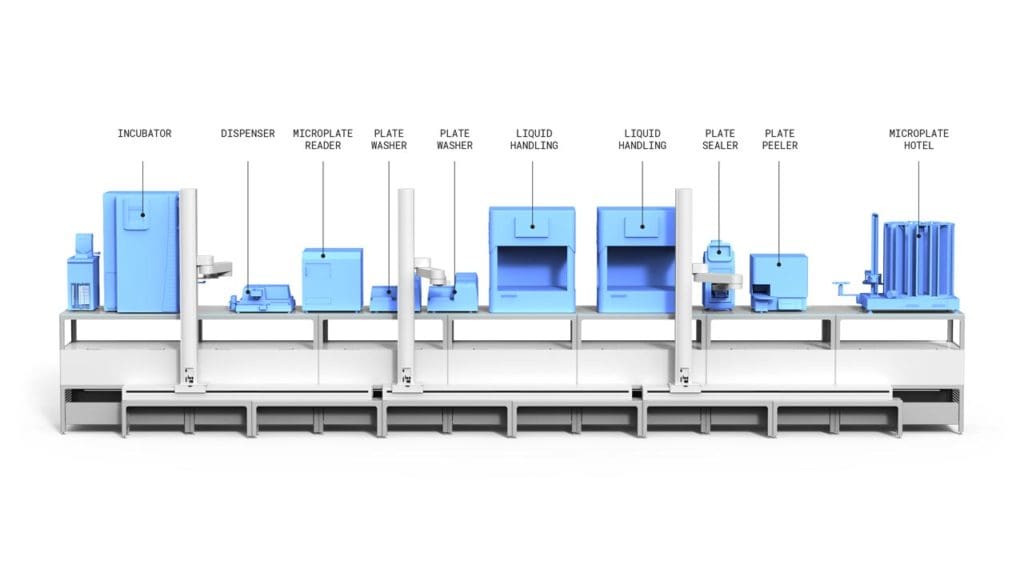
Implementing laboratory automation is a revolutionary approach to improving laboratory workflows that fully integrates with other approaches to workflow management. Laboratory procedures are often highly reliant on the manual operation of tools, reagents, and instruments by laboratory staff 6. This can lead to inefficiencies in lab workflow, including an increased human error rate and decreased quality of results 7. The automation of traditionally manual processes has been explored as a solution to this, leading to multiple benefits including workflow efficiency, reproducibility, and increased safety 6.
Even though the use of automation has been steadily increasing, fewer clinical and research labs have implemented automated processes in contrast to industrial laboratories, which have seen widespread adoption and many benefits 6. Continued investment in automation systems now means that lab automation is more accessible than ever, with many mid- to high-volume clinical laboratories capable of implementing total laboratory automation 7.
The LINQ platform from Automata is one such automation platform, which enables labs to fully automate their workflows. Book with our team to chat about LINQ.
Benefits of lab workflow management systems
Laboratory workflow management systems allow labs to address the inefficiencies within their processes and produce reliable, reproducible, and timely results. Lab automation, in particular, has many benefits within laboratory workflow. These include a reduction in human errors, improvements in reproducibility and safety, along with the ability for labs to scale up processes 6.
References
- Letelier P, Guzmán N, Medina G, et al. Workflow optimization in a clinical laboratory using Lean management principles in the pre-analytical phase. J Med Biochem. 2021;40(1):26-32. doi: 10.5937/jomb0-26055
- Inal TC, Ozturk OG, Kibar F, et al. Lean six sigma methodologies improve clinical laboratory efficiency and reduce turnaround times. J Clin Lab Anal. 2018;32(1):e22180. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22180
- Fryer AA, Smellie WSA. Managing demand for laboratory tests: a laboratory toolkit. J Clin Pathol. 2013;66(1):62-72. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2011-200524
- Lin C, Li L, Chen L, Pan Y, Guan J. Using Bottleneck Analysis to Examine the Implementation of Standard Precautions in Hospitals. Am J Infect Control. 2020;48(7):751–756. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2019.12.003
- Barbé B, Verdonck K, Mukendi D, et al. The Art of Writing and Implementing Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for Laboratories in Low-Resource Settings: Review of Guidelines and Best Practices. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10(11):e0005053. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005053
- Holland I, Davies JA. Automation in the Life Science Research Laboratory. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:571777. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.571777
- Yu HE, Lanzoni H, Steffen T, et al. Improving Laboratory Processes with Total Laboratory Automation. Lab Med. 2019;50(1):96-102. doi: 10.1093/labmed/lmy031